Ethereum: Your Complete Beginner’s Guide to the World’s Second-Largest Cryptocurrency
Introduction: Unlocking the World’s Second‑Largest Cryptocurrency
Ethereum is widely acknowledged as the world’s second‑largest cryptocurrency, second only to Bitcoin in market value—but that label doesn’t do justice to what it enables. Beyond its price, Ethereum is a platform: programmable, flexible, and foundational to a new digital economy. For newcomers who have perhaps heard of ETH but aren’t quite clear what makes it special, this guide aims to illuminate Ethereum’s purpose, its workings, and why it has become essential in conversations about decentralized technology.
What Is Ethereum and How Ethereum Works
Credit from The Engineering Projects
At the heart of Ethereum lies a blockchain network, similar in structure to Bitcoin’s. But Ethereum goes further—its ledger not only records transfers of value but also executes smart contracts, or self‑running programs. These contracts automatically carry out rules when conditions are met, without intermediaries.
Learning Ethereum fundamentals means understanding this programmable nature. Developers use languages like Solidity or Vyper to write contracts deployed on the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)—a decentralized runtime environment. Transactions pay gas fees in ETH to reward the nodes and validate code execution.
For example, you could set up a crowdfunding contract: if the campaign raises the target amount by a deadline, funds are released; otherwise they’re returned. The code handles it—no trusted third party involved. That’s how Ethereum democratizes trust and enables new kinds of digital cooperation.
World’s second-largest cryptocurrency Ethereum Explained in Simple Terms for First‑Time Users
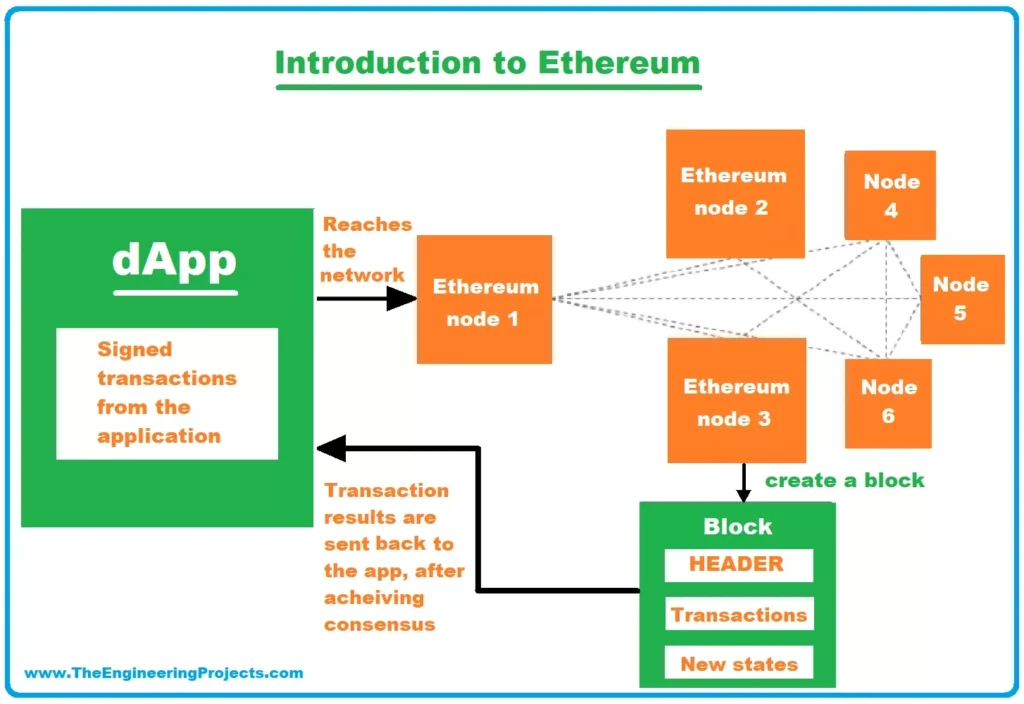
Credit from The Engineering Projects
For many beginners, the blockchain concept is abstract. Think of Ethereum as a world computer, one that anyone can interact with. Instead of trusting a centralized server or bank, you trust code stored on countless nodes around the world.
When someone creates a decentralized application (dApp)—say a game or lending platform—they write smart contracts. Users engage with the dApp via wallets like MetaMask, Trust Wallet, or hardware wallets such as Ledger or Trezor. Every user action—buying an NFT, staking crypto, swapping tokens—is recorded and processed via smart contract logic on Ethereum.
This model underlies DeFi platforms, NFT marketplaces, and DAO governance schemes. Ethereum explained at this level becomes accessible, even to users not building code—because interacting is as simple as sending ETH or signing transactions.
World’s second-largest cryptocurrency Ethereum 101 Guide: From Beginner to Confident User
A good Ethereum 101 guide walks newcomers through a few essentials:
- First, obtain ETH via a reputable exchange (Coinbase, Binance, Kraken, etc.), ensuring KYC, secure login, and two‑factor authentication are in place.
- Second, move ETH into your own wallet—not leaving significant funds on an exchange. Start with MetaMask or similar, familiarize with public key/address vs private key/seed phrase; back up carefully and never share them.
- Third, practice: small transactions, exploring dApps in test mode or with minimal funds. Understand that gas fees fluctuate—do not be alarmed if they rise sharply during high network demand.
Along the way, many new users ask: why buy Ethereum safely? It begins with secure exchange selection, careful wallet setup, and proper key hygiene. Only then can you explore NFTs, staking, or decentralized finance with confidence.
Ethereum vs Bitcoin: Key Differences Every Beginner Should Know
Both Bitcoin and ETH operate on blockchain, but they serve different roles. Bitcoin is primarily a store of value, often called “digital gold”; it’s transit‑focused, with a capped supply of 21 million coins. Ethereum, in contrast, is built for flexibility. It supports smart contracts, dApps, and financial innovation—without being limited to simple transactions.
From a beginner’s perspective:
- Purpose: Bitcoin is value transfer; Ethereum is programmable infrastructure.
- Speed & Functionality: Ethereum permits faster block times and complex contract execution.
- Monetary Policy: Bitcoin’s fixed cap versus Ethereum’s flexible issuance model, where supply is influenced by staking, burning gas fees, and ongoing protocol changes.
- Consensus: Ethereum now uses Proof of Stake (after “The Merge”), making it more energy‑efficient than Bitcoin’s Proof of Work.
This side‑by‑side comparison helps novices see why Ethereum is still widely seen as more than “just another coin”—it’s a platform for innovation.
How Ethereum Is Powering the Future of Decentralized Technology
Ethereum powers much of what is called Web3—a decentralized vision of the internet, built on blockchain. Whether it’s DeFi platforms like Uniswap or Compound, NFT ecosystems like OpenSea, or DAOs governing projects in tokenized ways, Ethereum underpins the architecture and logic.
Builders are exploring new frontiers: tokenizing real estate, creating decentralized identity systems, enabling micro‑transactions in virtual worlds, or attaching royalties automatically to digital art. Ethereum’s appeal lies in enabling trustless trust—with rules enforced by code, visible to all, but changeable only via consensus.
Its roadmap continues to evolve, with improvements like sharding, layer‑2 scaling solutions, and danksharding designed to reduce transaction costs and improve throughput. These advances aim to keep Ethereum at the forefront of decentralized innovation.
Safety, Challenges, and Ethereum Investment Tips

Credit from Rajput Jain & Associates
Ethereum remains volatile. Gas fees surge, dApps sometimes contain bugs, and new protocols come with risk. However, for beginners interested in investing or using ETH:
- Start small: Begin with modest amounts to learn.
- Diversify: ETH is only part of many decentralized portfolios.
- Stay informed: Follow official Ethereum Foundation updates, developer blogs, and community resources.
- Avoid phishing: Always verify URLs, don’t share secrets, and be cautious with browser prompts or unfamiliar dApps.
- Consider staking: If you plan to hold long‑term, staking ETH (solo or via pools) can earn rewards—but also locks funds for a period and carries risks.
Your complete beginner’s guide to using Ethereum should highlight caution as much as curiosity. Use Ethereum for growth, but treat it with respect.
Final Thoughts: Why Ethereum Remains the World’s Second‑Largest Cryptocurrency
As one looks across the crypto landscape, Ethereum emerges not merely as a coin, but as a vibrant ecosystem. From its inception in 2015 to recent upgrades like Proof of Stake and proto‑danksharding, Ethereum’s evolution reflects its ambition: to be the backbone of decentralized finance, governance, art, and community.
To understand Ethereum is to understand a new economic frontier. For beginners, that starts with modest steps—getting ETH securely, using a wallet, exploring dApps, and learning about smart contracts. But it ends with a broader realization: Ethereum is more than a currency. It is, and will remain, the world’s second‑largest cryptocurrency in value—and perhaps the most transformative blockchain platform humanity has brought into being.
By weaving the technology and the human stories together, this guide hopes to offer clarity—but also inspire. Because Ethereum isn’t in trend; it’s shaping tomorrow.




