Impermanent Loss in DeFi for Beginners: Understanding Risks and Rewards
Summary
- Introduction: What Is Impermanent Loss?
- The Mechanics Behind Impermanent Loss
- Practical Example of Impermanent Loss
- Observations from Real DeFi Markets
- Mitigation Strategies for Beginners
- Comparing Impermanent Loss with Other DeFi Risks
- Impermanent Loss Case Study: ETH/USDT Pool
- Conclusion & Key Takeaways
Introduction: Navigating Impermanent Loss in DeFi
Impermanent loss in DeFi for beginners is often one of the first hurdles faced when providing liquidity to decentralized finance platforms. Unlike a standard investment where asset value grows or declines linearly, impermanent loss emerges from the mechanics of automated market makers (AMMs). Simply put, it occurs when the relative prices of assets in a liquidity pool change, causing a discrepancy between the value of pooled assets and what you would have earned by holding them separately.
Recognizing how this works is vital, as DeFi continues to attract both retail and institutional investors.
The Mechanics Behind Impermanent Loss
Credit from Koinly
DeFi liquidity pools operate on AMMs, which maintain a constant ratio of deposited tokens. For example, in an ETH/USDC pool, the AMM automatically adjusts the number of ETH and USDC to maintain balance.
- If ETH’s price rises sharply against USDC, the pool’s ETH quantity decreases while USDC increases.
- When withdrawing, liquidity providers may receive fewer ETH than initially deposited, which can result in a lower total value compared to holding the tokens outside the pool.
This loss is termed “impermanent” because it may decrease or disappear if token prices return to their original levels, but it becomes permanent if you withdraw during a price divergence.
Practical Example of Impermanent Loss
| Asset Pair | Initial Deposit | Price Change | Value if Held | Value in Pool | Impermanent Loss (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ETH/USDC | 1 ETH + 2,000 USDC | ETH $2,500 → $3,000 | $5,000 | $4,850 | 3% |
| ETH/DAI | 1 ETH + 2,500 DAI | ETH $2,500 → $2,700 | $5,200 | $5,160 | 0.8% |
| USDC/DAI | 2,500 USDC + 2,500 DAI | Stable | $5,000 | $4,999 | ~0% |
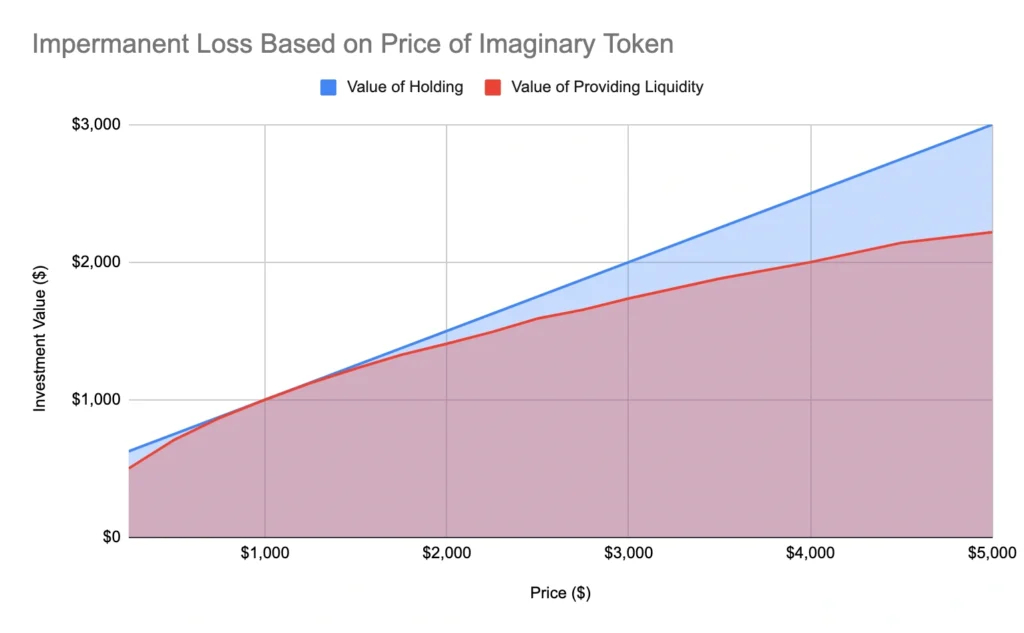
This table highlights how impermanent loss differs depending on asset volatility. Pairs with stablecoins experience negligible loss, while highly volatile pairs like ETH/USDC are more exposed.
Observations from Real DeFi Markets
Credit from Collective Shift
On platforms such as Uniswap and Curve, impermanent loss has been a consistent factor for liquidity providers. In 2021, ETH/USDC pools saw liquidity providers gain less than if they had held ETH alone during a bull run, even though they earned fees. Conversely, stablecoin pairs like USDC/DAI showed minimal loss, making them suitable for more conservative participants.
These examples emphasize that the choice of assets significantly impacts the exposure to impermanent loss.
Mitigation Strategies for Beginners
While impermanent loss cannot be completely avoided, strategies exist to minimize its effect:
- Stablecoin Pools: Pairing assets with minimal volatility reduces impermanent loss.
- Diversified Pools: Allocating liquidity across multiple pools or asset types spreads risk.
- Timing Participation: Entering pools during low-volatility periods can lessen initial loss exposure.
- Fee and Incentive Offsets: Some protocols offer high trading fees or token rewards that compensate for impermanent loss.
Careful monitoring of pool performance and market trends can help manage risk effectively.
Comparing Impermanent Loss with Other DeFi Risks

Credit from Emurgo
It’s important for beginners to differentiate impermanent loss from other DeFi-related risks:
- Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: Bugs can result in total loss of funds.
- Rug Pulls: Developers withdrawing liquidity unexpectedly.
- Market Risk: Broad asset depreciation affects both pooled and held assets.
Unlike impermanent loss, these risks are external and less predictable, emphasizing the need for due diligence and security awareness.
Impermanent Loss in DeFi Case Study: ETH/USDT Pool in 2022
During ETH’s price volatility in mid-2022, liquidity providers in ETH/USDT pools experienced modest impermanent loss. Despite partial recovery, providers who relied solely on fee rewards or governance tokens mitigated some of their losses. This scenario illustrates how combining yield opportunities with pool selection strategies can reduce net negative impacts from impermanent loss.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways for Beginners
Impermanent loss in DeFi for beginners may seem complex at first glance, but understanding its mechanism, observing real-world examples, and applying risk mitigation strategies can make it manageable. Selecting appropriate pools, diversifying assets, and leveraging incentive structures are essential steps to optimize liquidity provision. Awareness and strategic planning transform impermanent loss from an unpredictable threat into a calculated factor within DeFi participation.




