Token Burning in Crypto: A Beginner’s Guide to Understanding Coin Destruction
Summary
Introduction: What Is Token Burning?
Token burning in crypto refers to the process of permanently removing a certain number of cryptocurrency tokens from circulation. This is typically done by sending them to a “burn address”—a wallet that no one controls or has access to. Once sent, these tokens are effectively destroyed and cannot be retrieved or used again.
The primary goal of token burning is to reduce the total supply of a cryptocurrency, potentially increasing its scarcity and, in turn, its value. This practice is akin to a company buying back its own shares to reduce supply and potentially increase the value of remaining shares.
How Token Burning Works
Credit from Trust Wallet
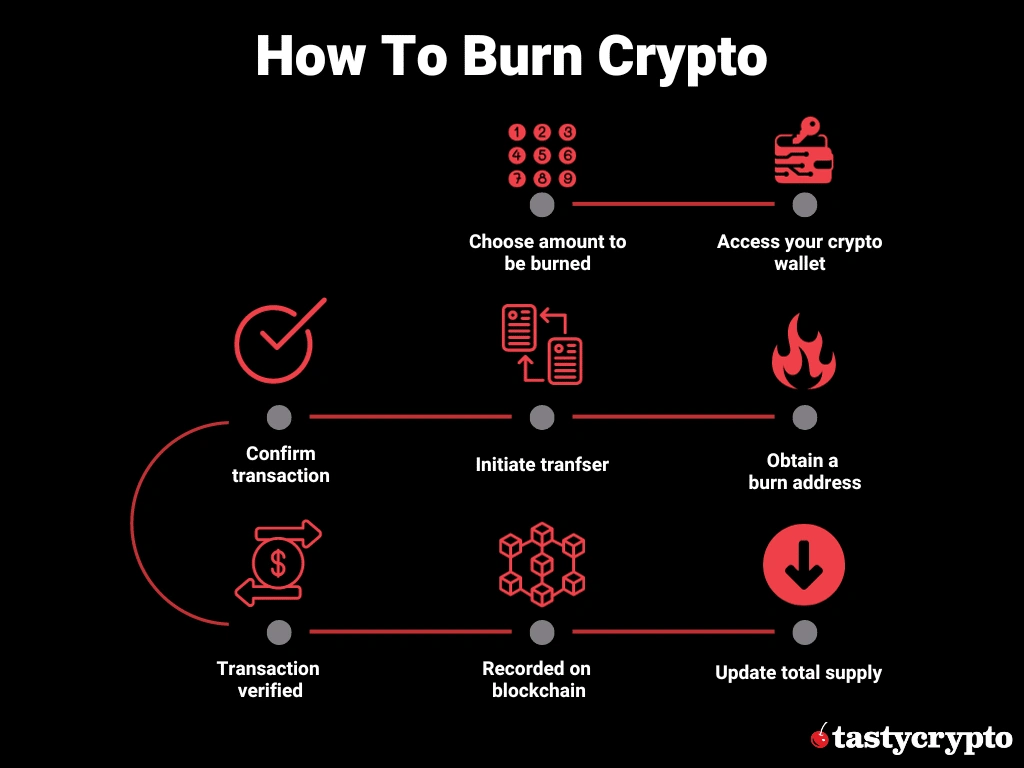
The mechanics of token burning are straightforward:
- Selection of Tokens:
The project team or community decides on the number of tokens to burn. This decision can be based on various factors, such as reducing inflation or increasing scarcity. - Sending to a Burn Address:
The selected tokens are transferred to a burn address. This address is publicly known but has no private key, making it impossible to access the tokens once sent. - Blockchain Verification:
The transaction is recorded on the blockchain, providing transparency and allowing anyone to verify the burn. - Updated Supply Metrics:
After the burn, the total supply of the cryptocurrency is reduced, which can be reflected in various blockchain explorers and analytics platforms.
Why Do Cryptocurrencies Burn Tokens?
Cryptocurrency projects burn tokens for several reasons:
- Reducing Supply:
By decreasing the total number of tokens in circulation, burning can create scarcity, potentially increasing the value of the remaining tokens. - Controlling Inflation:
For cryptocurrencies with high inflation rates, burning can help offset the issuance of new tokens, maintaining the value of existing ones. - Enhancing Value Proposition:
Regular burns can signal to investors that the project is committed to maintaining or increasing the value of its token. - Community Engagement:
Some projects involve their communities in the burning process, allowing token holders to participate in decisions about token supply.
Real-World Examples of Token Burning

Credit from tastycrypto
1. Binance Coin (BNB)
Binance conducts quarterly burns of BNB to reduce its total supply. The amount burned is based on the trading volume on the Binance exchange. For instance, in Q1 2025, Binance burned approximately 2.1 million BNB, valued at over $500 million USD at the time.
2. Ethereum (ETH)
With the implementation of EIP-1559 in August 2021, Ethereum introduced a mechanism where a portion of transaction fees is burned. This has led to a significant reduction in ETH’s supply over time. As of mid-2025, over 4 million ETH have been burned since the upgrade.
3. Shiba Inu (SHIB)
Shiba Inu’s community has been actively involved in burning tokens. In May 2021, Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin burned approximately 410 trillion SHIB tokens, worth about $6.7 billion at the time. Additionally, the Shiba Inu team introduced the ShibaSwap platform, allowing users to burn tokens voluntarily in exchange for rewards.
Table: Token Burning Examples in Practice
| Cryptocurrency | Burn Mechanism | Total Burned (Approx.) | Purpose/Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Binance Coin | Quarterly burns by Binance | 2.1M BNB (Q1 2025) | Reduce supply to 100M, increase scarcity |
| Ethereum | EIP-1559 fee burn | 4M+ ETH (as of 2025) | Fee deflation, balancing issuance |
| Shiba Inu | Community & burn portals | 410T+ SHIB (2021) | Reduce massive supply, support scarcity |
Sources: Binance announcements, ultrasound.money, Shiba Inu burn portal stats
Benefits and Limitations of Token Burning
Benefits
- Increased Scarcity:
Reducing the supply of tokens can make them more scarce, potentially increasing their value. - Inflation Control:
Burning can help offset the effects of new token issuance, maintaining the value of existing tokens. - Community Trust:
Regular and transparent burns can build trust within the community and among investors.
Limitations
- No Guaranteed Price Increase:
While burning can reduce supply, it doesn’t guarantee that demand will increase, and thus, the price may not rise. - Potential for Manipulation:
If not done transparently, burning can be perceived as a tactic to manipulate the market. - Resource Intensive:
For some projects, the process of burning tokens can be resource-intensive and may require significant coordination.
Token Burning vs. Other Supply Management Methods
While token burning is a popular method for managing supply, it’s not the only strategy:
- Staking:
Users lock up their tokens to participate in network operations, reducing the circulating supply. - Buybacks:
Projects purchase their own tokens from the market to reduce supply without burning them. - Halving Events:
In some cryptocurrencies, the reward for mining new blocks is halved at regular intervals, reducing the rate of new token issuance.
Each method has its advantages and is chosen based on the project’s goals and the economic model it follows.
Conclusion
Credit from tastycrypto
Token burning in crypto is a strategic mechanism used by projects to manage supply, control inflation, and potentially increase the value of their tokens. While it offers several benefits, it’s essential for investors to understand the broader context and not view burning as a guaranteed path to price appreciation. As the crypto space continues to evolve, token burning remains a fundamental aspect of many projects’ economic models.




